Warning: Deprecated articles
You are using the old version of the knowledge base for ERPConnect.
Make sure to use the samples within the new HelpCenter for ERPConnect.
This section shows how to create, register and use RFC server functions.
About #
In the following application sample a simple RFC server function is created that allows ABAP programs to add numbers.
Two input parameters (NUMBER1 and NUMBER2) are added and result (RES) is passed back to the calling ABAP program.
Register the RFC Server Function #
- Initialize an RFCServer object by providing the gateway host, the gateway service and the program ID to register on the SAP gateway. For this, the program ID must be available as a registered destination in SAP, see Setting Up an RFC Destination.
- Use the method RegisteredFunctions.Add to register an RFCServerFunction object. An RFCServer object can hold more than one RFCServerFunction object.
- Add Imports and Exports. They are handled the same way as when calling RFC functions as a client.
- When an ABAP program calls the function, the event IncomingCall is triggered. If you use C#, you must define the event call-back with a separate line of code.
- Start the server with Start.
Note: If the RFC destination is set to Unicode (SAP transaction code SM59), the property IsUnicode of the RFCServer object must be set to true.
using ERPConnect;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
RFCServer s = new RFCServer();
s.GatewayHost = "sap-erp-as05.example.com";
s.GatewayService = "sapgw11";
s.ProgramID = "ERPTEST";
s.IncomingCall+=new ERPConnect.RFCServer.OnIncomingCall(s_IncomingCall);
RFCServerFunction f = s.RegisteredFunctions.Add("Z_ADD");
f.Imports.Add("NUMBER1",RFCTYPE.INT);
f.Imports.Add("NUMBER2",RFCTYPE.INT);
f.Exports.Add("RES",RFCTYPE.INT);
s.Start();
Console.Write( "Server is running. Press any key to exit.");
Console.ReadLine();
}
Handle Incoming Calls #
The following code shows how the IncomingCall event is handled:
private static void s_IncomingCall(RFCServer Sender, RFCServerFunction CalledFunction)
{
if (CalledFunction.FunctionName=="Z_ADD")
{
Int32 i1 = (Int32)CalledFunction.Imports["NUMBER1"].ParamValue;
Int32 i2 = (Int32)CalledFunction.Imports["NUMBER2"].ParamValue;
Int32 erg = i1 + i2;
CalledFunction.Exports["RES"].ParamValue = erg;
Console.WriteLine("Incoming Call");
}
Else
throw new ERPConnect.ERPException("Function unknown");
}
The import parameters are passed by the calling SAP system.
The export parameters are passed back to SAP.
Call RFC Server Functions in ABAP #
In this example the following ABAP code is used to call the new function Z_ADD in the remote destination ERPTEST.
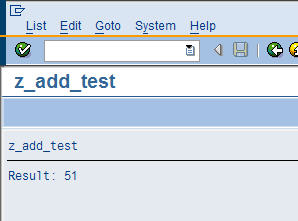
The two numbers 26 and 25 are passed, and the result 51 is passed back.
REPORT z_add_test
.
DATA result TYPE i.
CALL FUNCTION 'Z_ADD' DESTINATION 'ERPTEST'
EXPORTING
number1 = 26
number2 = 25
IMPORTING
res = result.
WRITE: / 'Result: ', result.
The screenshot below shows the running ABAP program: