In the following we demonstrate the Talend integration via a REST web service call. In Talend we execute an extraction via an HTTP Request.
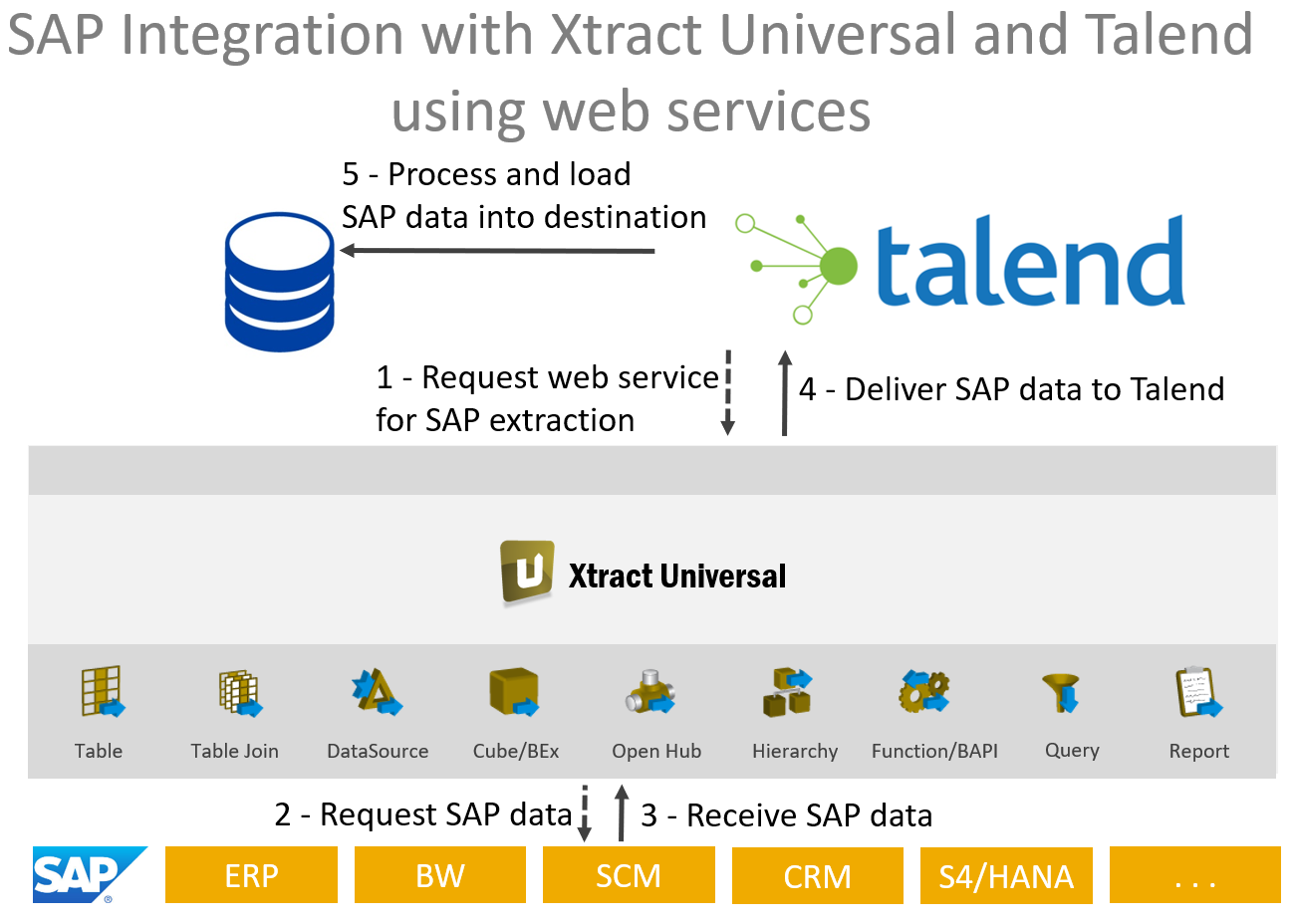
The following image depicts the architecture. Xtract Universal extracts the data from SAP and delivers it via REST web service in a csv format. Json format would also be another possible option.
We can subsequently process the data in Talend, e.g., write the extracted data into a database.
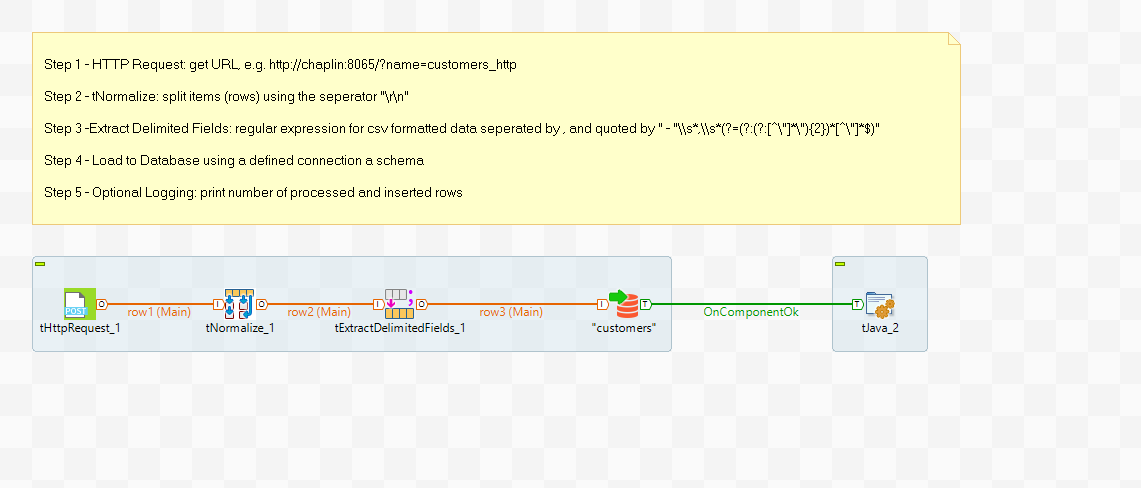
Job Overview in Talend #
The job overview in Talend shows the used steps. There are five steps that are described in detail:
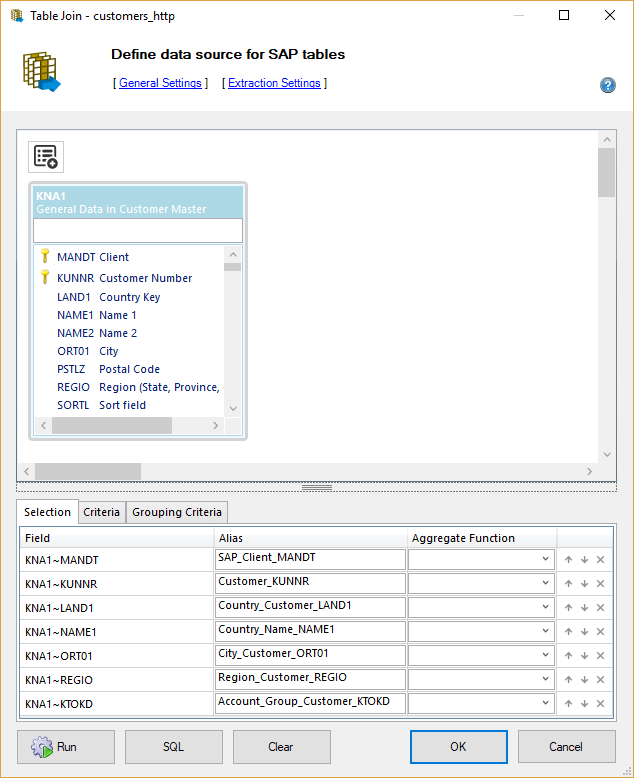
Extraction in Xtract Universal #
In the following we can see the definition of the extraction in Xtract Universal. We extract customer data from the SAP table KNA1:
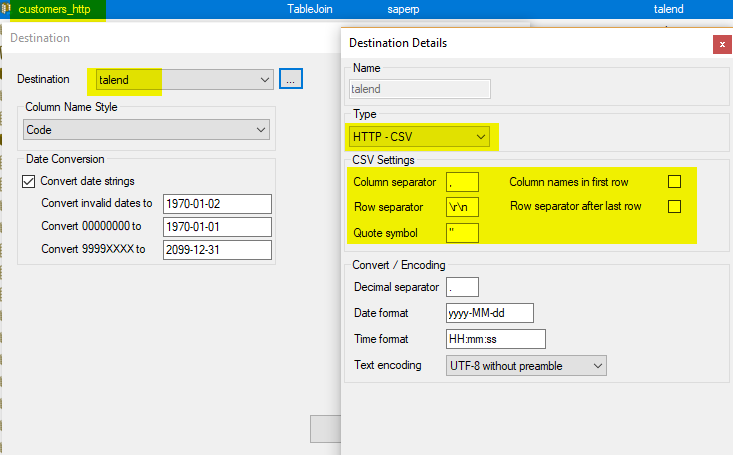
In Xtract Universal we have defined an extraction with web service in csv format as a destination (HTTP-CSV).
The destination settings for HTTP-CSV offer options to deliver data without a column name and a line separator after the last line. We chose this option in the presented example.
SQL Server #
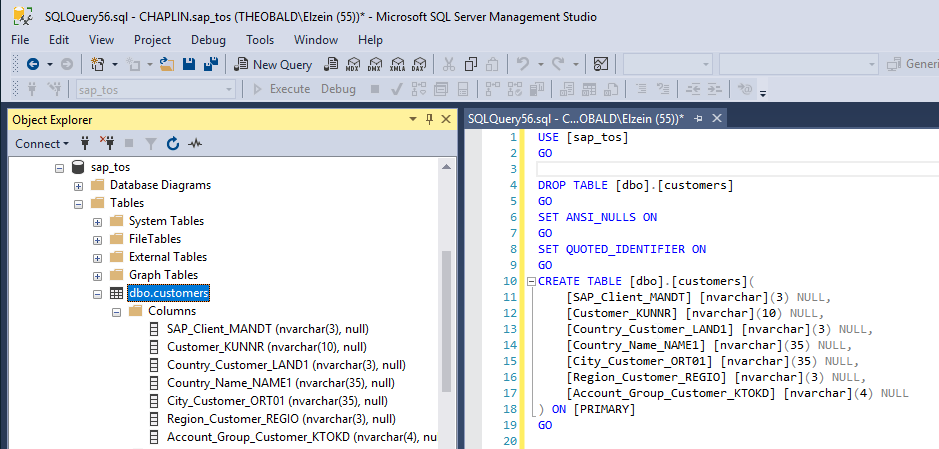
We created a target table on the SQL server with the following SQL command. The created table is used to load the data later on.
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[customers](
[SAP_Client_MANDT] [nvarchar](3) NULL,
[Customer_KUNNR] [nvarchar](10) NULL,
[Country_Customer_LAND1] [nvarchar](3) NULL,
[Country_Name_NAME1] [nvarchar](35) NULL,
[City_Customer_ORT01] [nvarchar](35) NULL,
[Region_Customer_REGIO] [nvarchar](3) NULL,
[Account_Group_Customer_KTOKD] [nvarchar](4) NULL
) ON [PRIMARY]
Created table on the SQL Server:
Xtract Universal also offers a web service for the metadata (i.e. column names and data types) of an extraction. Check the online help for further information.
Talend #
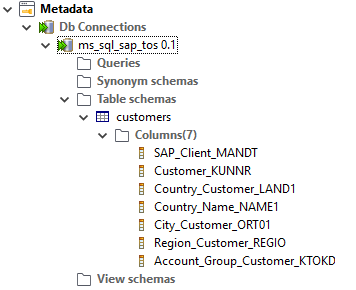
Before defining the steps in Talend, we defined a connection to the SQL server (under Meta data > DB Connections) and the table schema.
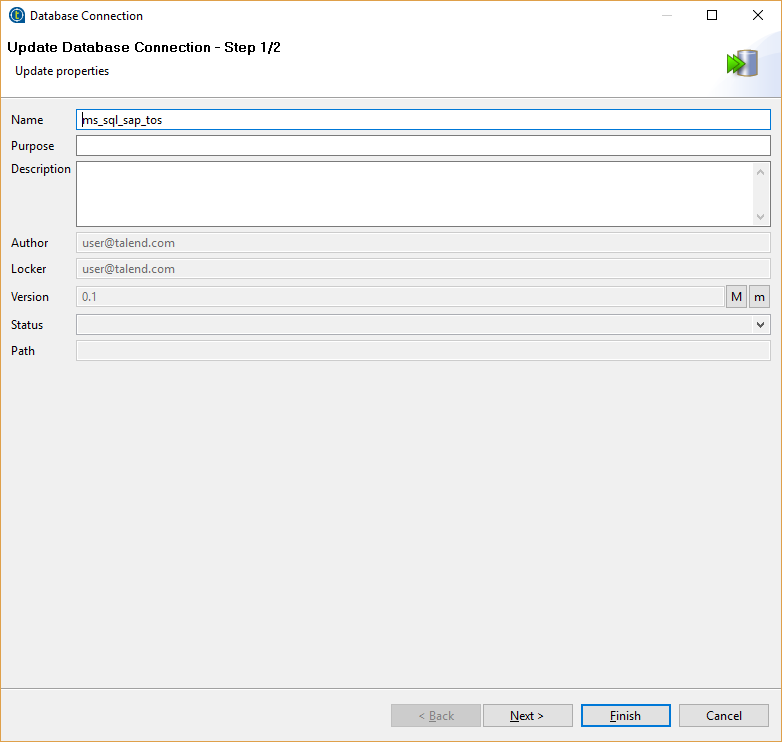
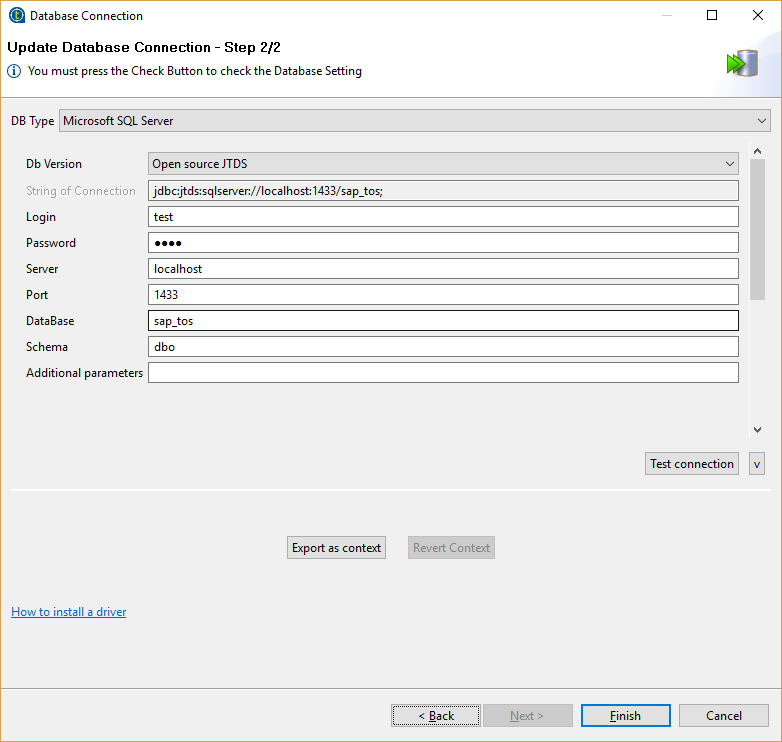
Table Schema:
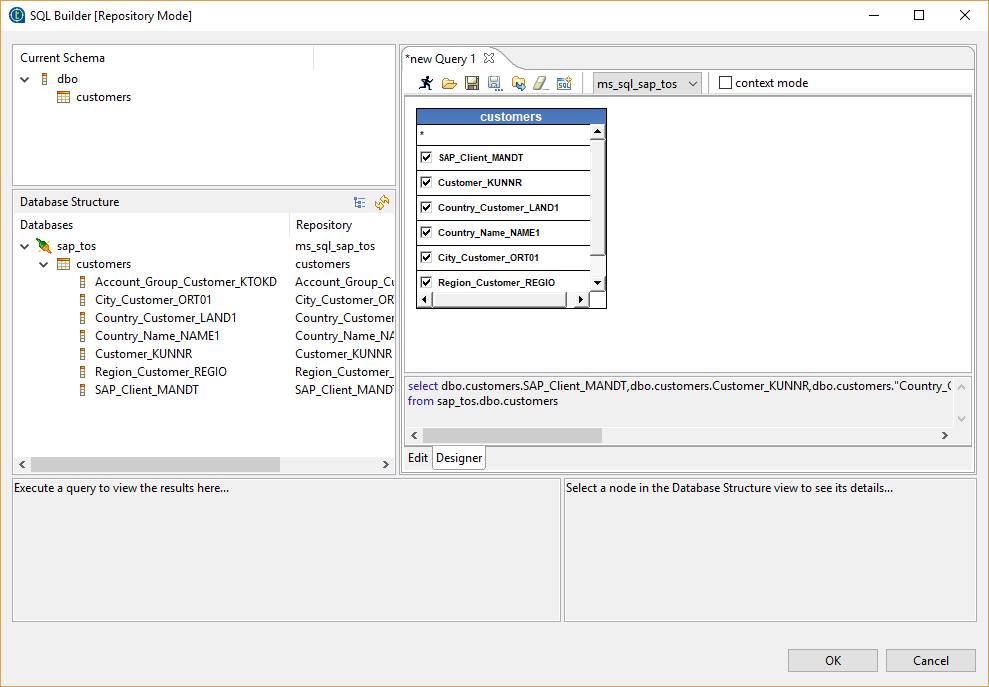
Overview of the meta data definition:
Checking the Talend Job #
Now we can check the settings of the five steps in the Talend job.
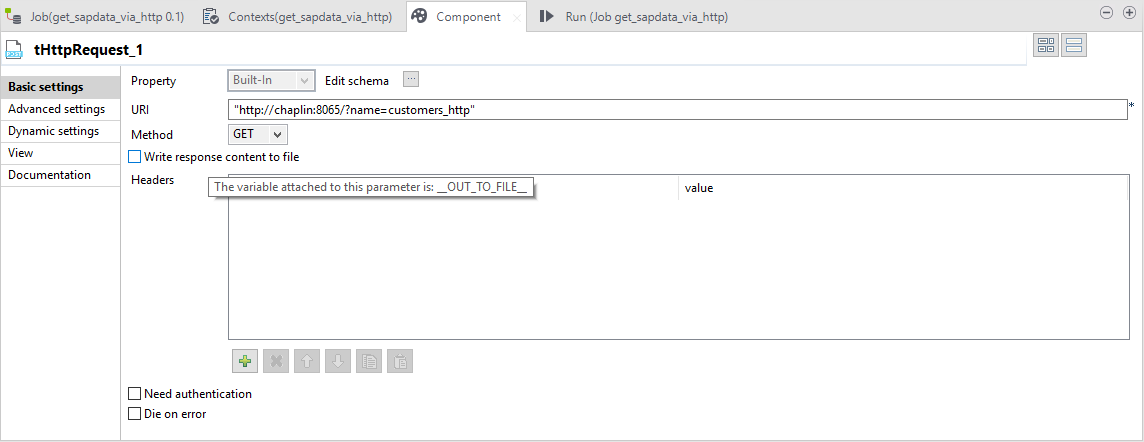
Step 1 - HTTP Request
In the fist step we execute the HTTP Request.The URI parameter is passed on: http://chaplin:8065/?name=customers_http.
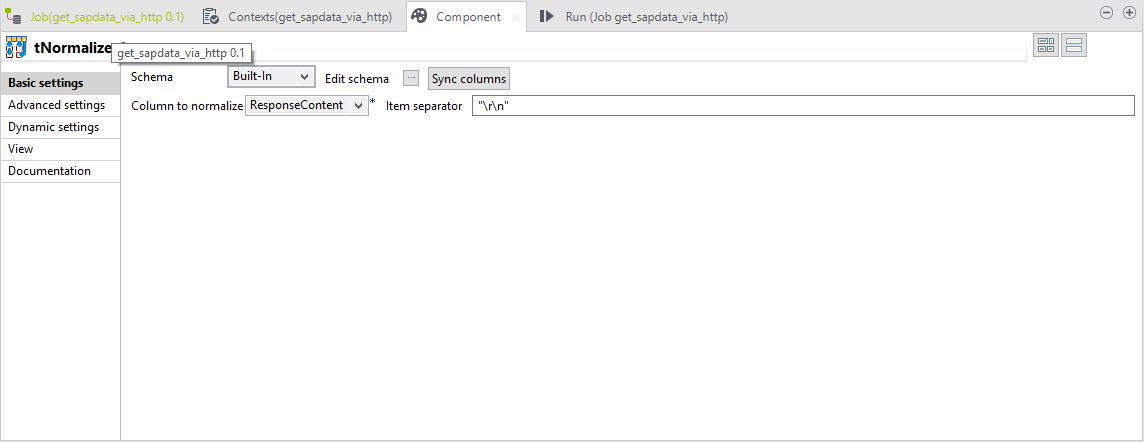
Step 2 - Line Splitting
The data is split into lines using the line break symbols “\r\n”.
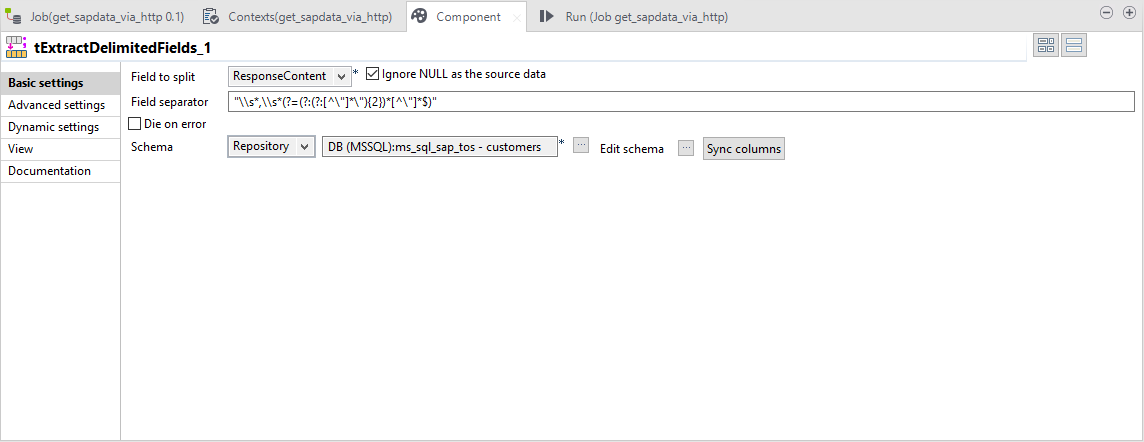
Step 3 - Column Splitting
Data sets are split into columns using the regular expression: \\s*,\\s*(?=(?:(?:[^\"]*\"){2})*[^\"]*$)
We use the previously defined schema for the columns.
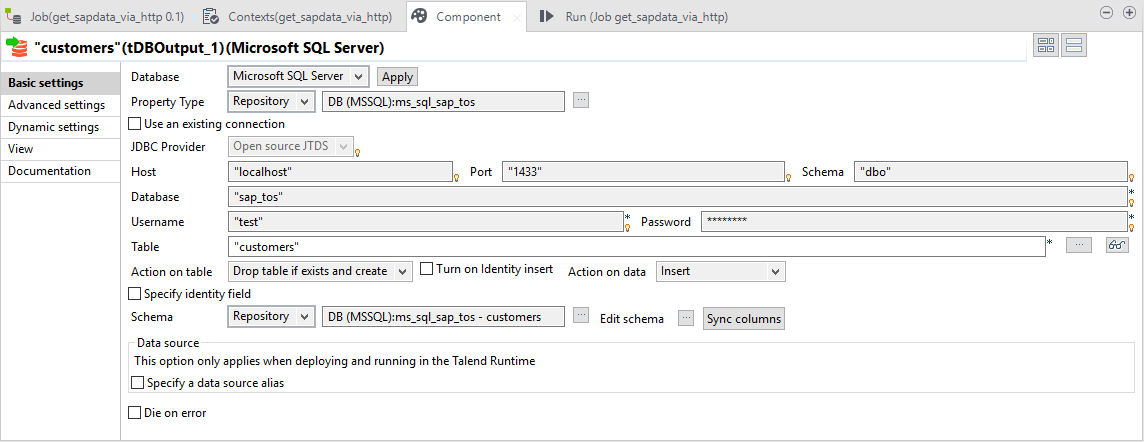
Step 4 - Writing into the Database
Now we can write the data into the SQL table. To do so, we use the connection and the schema that we defined in the beginning:
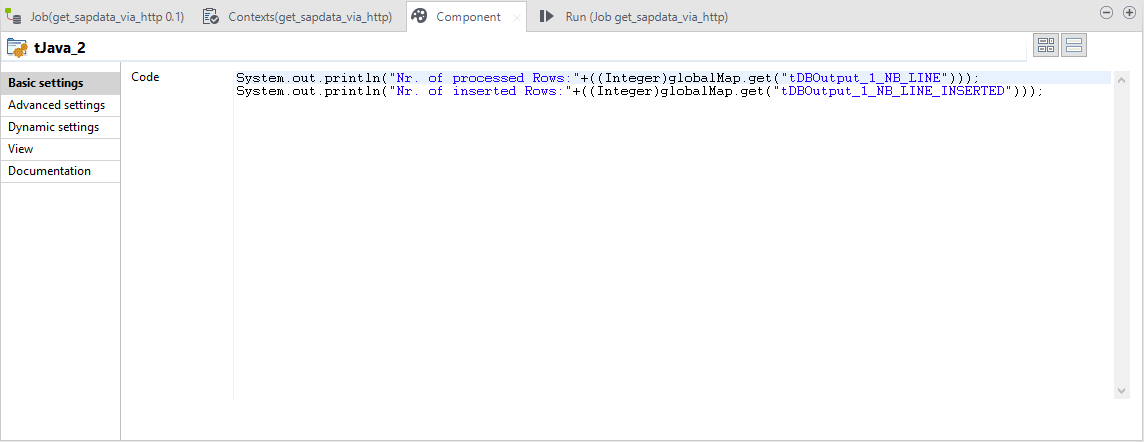
Step 5 - Logging (optional)
In the following optional step we use a Java component to log the number of the processed data sets in case of a successful operation.
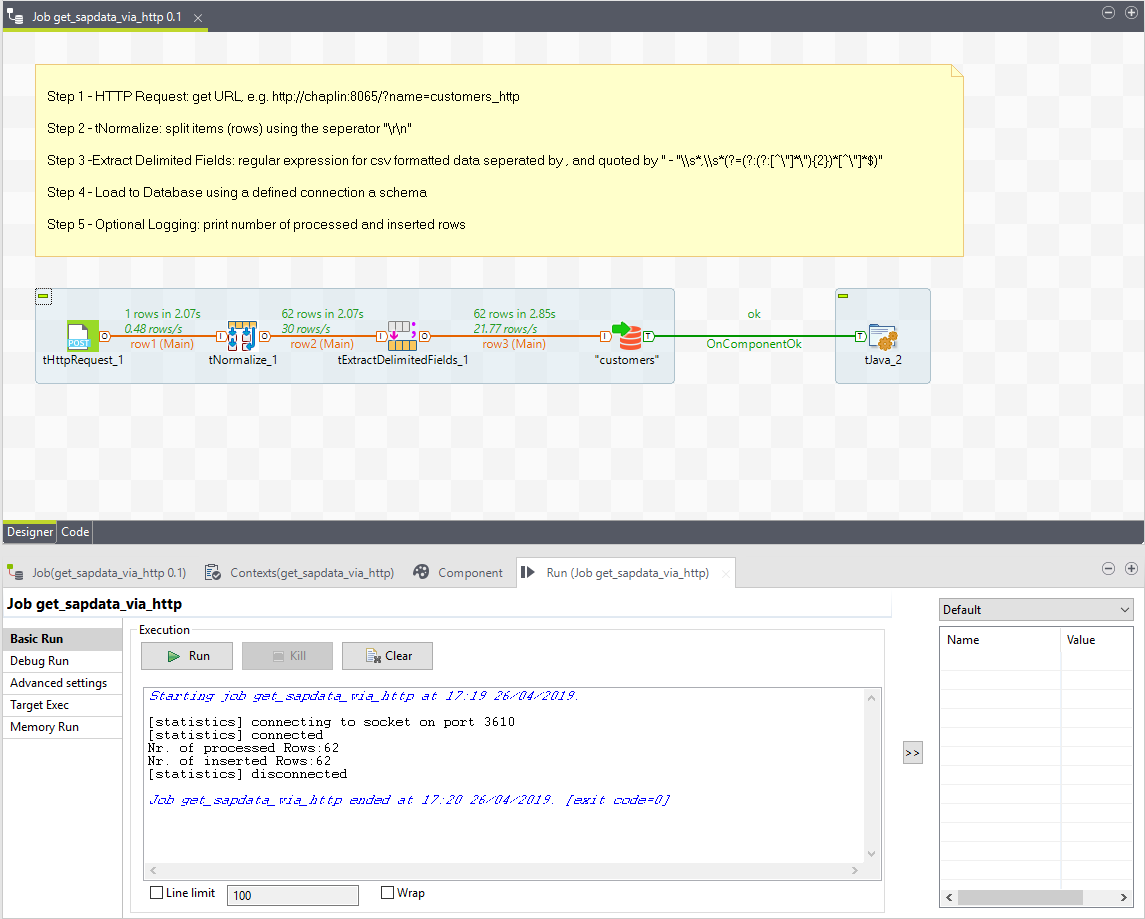
Job Execution
Now we can execute the job. The job is successful and the customer data sets are extracted from SAP and are written to the SQL server.
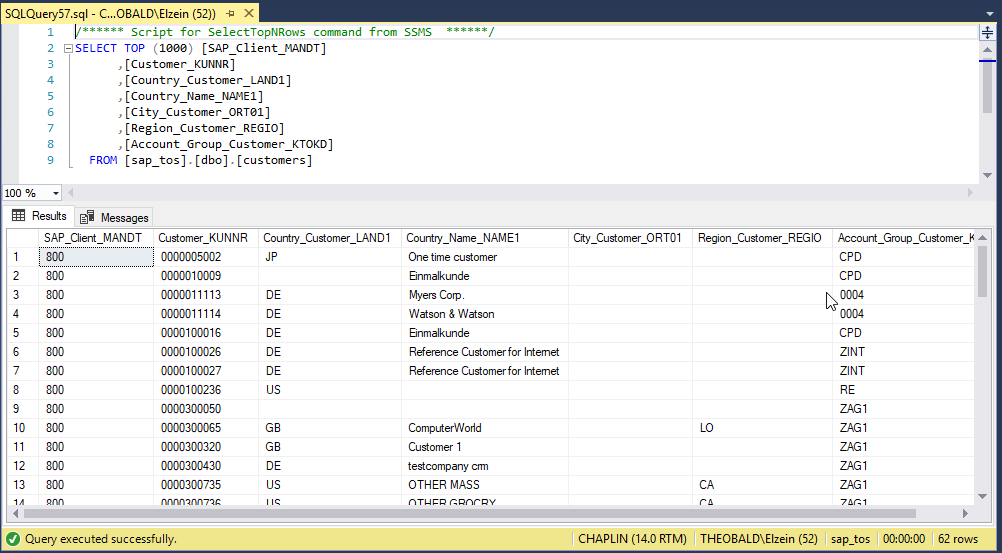
Checking the Result on the SQL Server #
Now we can check the result on the SQL server.
In the presented article we depicted how one can call SAP extractions provided by Xtract Universal via HTTP and further process them using Talend.